Parse AI
How to Scrape Amazon Prices (all code included)
Web scraping guide for beginners to collect prices from products on amazon.com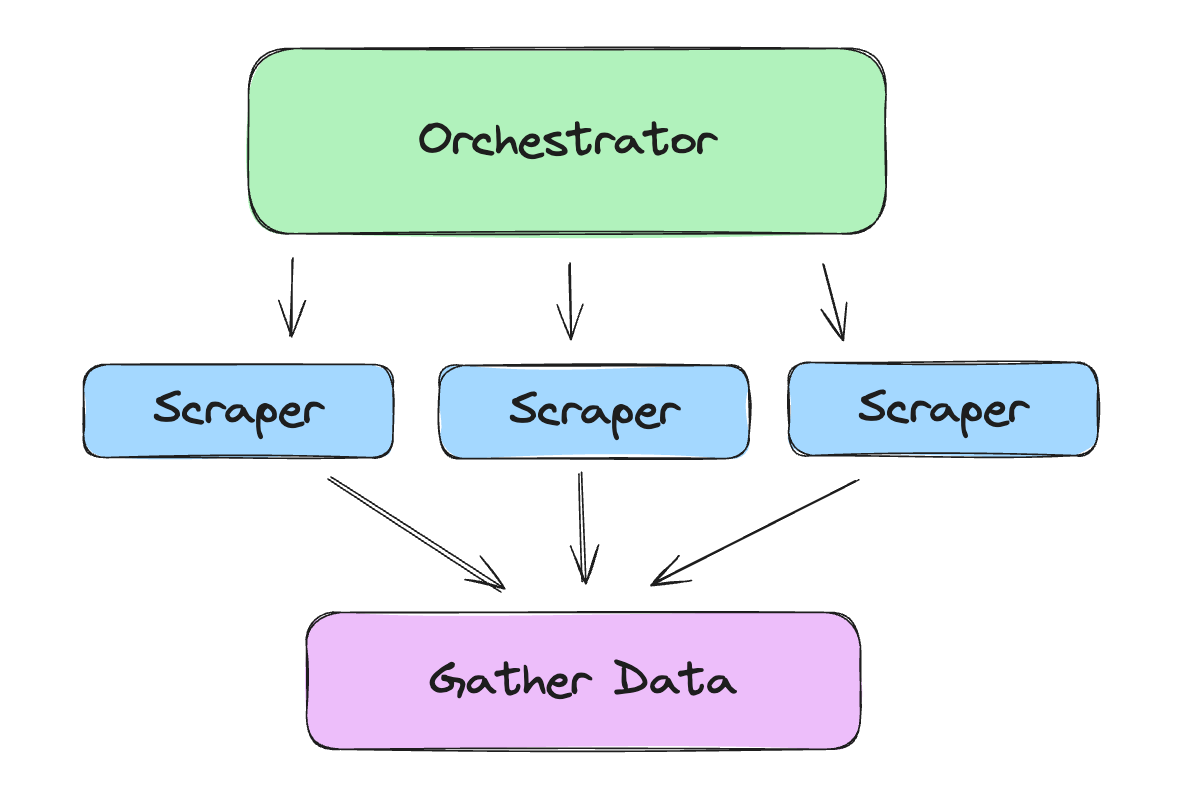 Anyone can set up a web scraper in just a few minutes, no matter their level of coding experience.
Anyone can set up a web scraper in just a few minutes, no matter their level of coding experience.
This is a simple guide for beginners on how to scrape prices from amazon.com (with some bonus intermediate steps to scrape many products at scale).
Note: Feel free to reach out to me here if you have any need for web data, data pipelines, or AI tools to help your data intake :)
Prerequisites:
Python installed on your computer
An IDE of your choice (I prefer PyCharm for Python projects, although I use Cursor heavily as well)
If you’d like all the code for this project, I set up a GitHub repo with everything ready to go :)
Step #0: Set up your environment and install dependencies
For this project I’m using uv as my package manager, but feel free to use any package manager you prefer (like pip or poetry). If you don’t have uv installed, you can run pipx install uv or pip install uv to get started.
Then, go ahead and install the two dependencies we will use with these commands.
uv add curl-cffi
uv add beautifulsoup4Step #1: Choose an Amazon product to test your scraper on and find the ASIN
Amazon actually makes it quite easy to navigate product URLs on their site, because you can simply use the pattern https://amazon.com/dp/{ASIN} to navigate to any URL.
The “ASIN” is the “Amazon Standard Identification Number” of a product. You can find it by navigating to any product on amazon.com and looking for the ID directly after /dp/ in the url.
For example, I searched for iPhone cases and clicked on this product. The URL of the web page I was taken to was quite long:
https://www.amazon.com/Mkeke-Compatible-Not-Yellowing-Military-Grade-Protection/dp/B0FFGW3481?crid=33242U4CJGNNT&dib_tag=se&keywords=phone%2Bcase%2Biphone%2B17%2Bpro&qid=1759094060&sprefix=phone%2Bcase%2Caps%2C173&sr=8-3&th=1However, if you extract the ASIN from that long url here:
Press enter or click to view image in full size
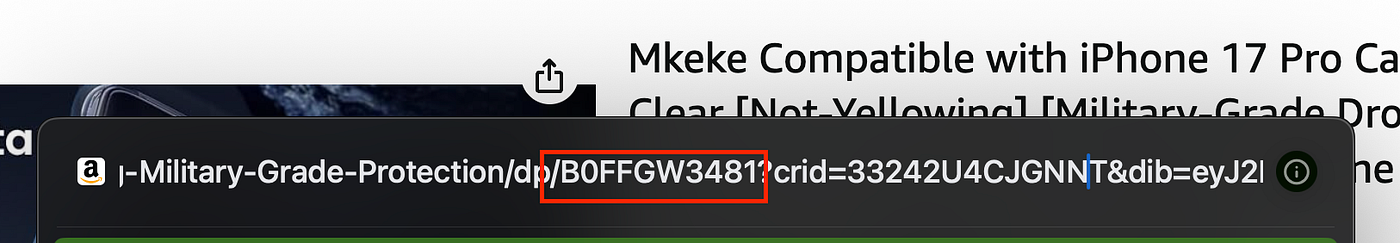
And then navigate to this URL:
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0FFGW3481You end up in the exact same spot!
Choose any product you want to scrape for this guide and make sure to note it’s ASIN.
Step #2: Set up your scraper
Time to start scraping.
We’ll start by sending a request to our URL using curl_cffi . This specific HTTP client allows us to impersonate browser TLS fingerprints, making it easier to avoid blocking mechanisms.
# price_scraper.py
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from curl_cffi import requests
async def price_scraper(url: str):
# Create a session, send a request, and soupify the HTML
session = requests.AsyncSession()
res = await session.get(url, impersonate="chrome")
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, "html.parser")
print(soup.prettify()[:1000])
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
url = "https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0FFGW3481"
product_data = asyncio.run(price_scraper(url))In this snippet we’re sending a request to the product page hoping to get back the base HTML. You can run this code in your IDE or by pasting this command in the terminal: python price_scraper.py .
Now that we have the HTML, we want to parse it to find the product price, and product title.
I prefer to use CSS selectors with BeautifulSoup to parse through HTML. Here’s a cheatsheet you can use if you are unfamiliar with CSS selectors.
Add in a few lines to grab the product_title , product_price_whole (the dollar amount) and product_price_fraction (the cents amount). Then combine the dollars and cents and cast to a float .
# price_scraper.py
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from curl_cffi import requests
async def price_scraper(url: str):
# Create a session, send a request, and soupify the HTML
session = requests.AsyncSession()
res = await session.get(url, impersonate="chrome")
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, "html.parser")
print(soup.prettify()[:1000])
# Grab the product title and price
product_title = soup.select_one("span#productTitle").text.strip()
product_price_whole = soup.select_one("div#corePriceDisplay_desktop_feature_div span.a-price-whole").text.strip()
product_price_fraction = soup.select_one("span.a-price-fraction").text.strip()
# Remove any commas from the whole part of the price
product_price_whole = product_price_whole.replace(",", "")
# Combine the dollars and cents to form the full price
product_price = float(product_price_whole + product_price_fraction)
data = {
"title": product_title,
"price": product_price,
"url": url
}
return data
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
import json
url = "https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0FFGW3481"
product_data = asyncio.run(price_scraper(url))
print(json.dumps(product_data, indent=2))After running the code you should get a clean set of freshly scraped product data!
{
"title": "Mkeke Compatible with iPhone 17 Pro Case Clear [Not-Yellowing] [Military-Grade Drop Protection] Shockproof Protective Phone Bumper for Apple 6.3 inch 2025",
"price": 9.99,
"url": "https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0FFGW3481"
}You have now successfully scraped prices from amazon.com 🎉
Now onto some bonus steps to collect and scrape products at scale.
What if you wanted to track prices from hundreds or thousands of products on Amazon? You’ll need a way to collect product URLs and then feed them into the price scraper.
For this guide, we’ll execute a search query on Amazon and then collect the URLs that result from the search. Once we have all the URLs we’ll scrape them in parallel.
Step #3: Scrape product URLs based on a search query
# url_scraper.py
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from curl_cffi import requests
async def url_scraper(search_query: str, max_pages: int = None) -> list[str]:
# Send a request with a search query and soupify the HTML
params = {
"k": search_query
}
base_url = "https://www.amazon.com/s"
session = requests.AsyncSession()
res = await session.get(base_url, params=params, impersonate="chrome")
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, "html.parser")
# Use regex to find {"totalResultCount":\d+}
num_results = re.search(r'"totalResultCount":(\d+)', res.text).group(1)
if not num_results:
raise ValueError("No results found for the brand search.")
num_results = int(num_results)
print(f"Found {num_results} results for query: {search_query}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
query = "2024 macbook pro m4 max 16 inch"
results = asyncio.run(url_scraper(query))When you run this code, you should see a log printed with the number of results:
Found 584 results for query: 2024 macbook pro m4 max 16 inchNow let’s identify where the ASINs are for the products and gather the URLs:
# url_scraper.py
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from curl_cffi import requests
async def url_scraper(search_query: str, max_pages: int = None) -> list[str]:
# Send a request with a search query and soupify the HTML
params = {
"k": search_query
}
base_url = "https://www.amazon.com/s"
session = requests.AsyncSession()
res = await session.get(base_url, params=params, impersonate="chrome")
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, "html.parser")
# Use regex to find {"totalResultCount":\d+}
num_results = re.search(r'"totalResultCount":(\d+)', res.text).group(1)
if not num_results:
raise ValueError("No results found for the brand search.")
num_results = int(num_results)
print(f"Found {num_results} results for query: {search_query}")
# Find the ASINs and create the product URLs
items = soup.select('div[role="listitem"][data-component-type="s-search-result"]')
amazon_product_url = "https://www.amazon.com/dp/"
product_urls = list(set([amazon_product_url + x.get("data-asin") for x in items]))
print(f"Found {len(product_urls)} product URLs on the first page")
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
query = "2024 macbook pro m4 max 16 inch"
results = asyncio.run(url_scraper(query))Running this code prints an additional log:
Found 21 product URLs on the first pageFinally, let’s add pagination and gather every possible unique product URL from our search query.
# url_scraper.py
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from curl_cffi import requests
async def url_scraper(search_query: str, max_pages: int = None) -> list[str]:
# Send a request with a search query and soupify the HTML
params = {
"k": search_query
}
base_url = "https://www.amazon.com/s"
session = requests.AsyncSession()
res = await session.get(base_url, params=params, impersonate="chrome")
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, "html.parser")
# Use regex to find {"totalResultCount":\d+}
num_results = re.search(r'"totalResultCount":(\d+)', res.text).group(1)
if not num_results:
raise ValueError("No results found for the brand search.")
num_results = int(num_results)
print(f"Found {num_results} results for query: {search_query}")
# Find the ASINs and create the product URLs
items = soup.select('div[role="listitem"][data-component-type="s-search-result"]')
amazon_product_url = "https://www.amazon.com/dp/"
product_urls = list(set([amazon_product_url + x.get("data-asin") for x in items]))
print(f"Found {len(product_urls)} product URLs on the first page")
# Calculate the number of pages in order to paginate and collect more URLs
num_per_page = len(product_urls)
num_pages = (num_results // num_per_page) + (
1 if num_results % num_per_page > 0 else 0
)
# Paginate and repeat the process for each page
for page in range(2, num_pages + 1):
print(f"Fetching page {page} of {num_pages}")
params["page"] = page
res = await session.get(base_url, params=params, impersonate="chrome")
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, "html.parser")
items = soup.select(
'div[role="listitem"][data-component-type="s-search-result"]'
)
product_urls.extend(
list(set([amazon_product_url + x.get("data-asin") for x in items]))
)
# If you only want to scrape a certain number of pages, pass in max_pages
if max_pages and page >= max_pages:
break
all_product_urls = list(set(product_urls))
return all_product_urls
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
query = "2024 macbook pro m4 max 16 inch"
results = asyncio.run(url_scraper(query))
print(f"Found {len(results)} links for query: {query}")Nice! Now, that we have a scraper to collect URLs, we can feed those into our price scraper.
Step #4: Orchestrate collecting URLs and feed them into the price scraper
We can take advantage of asyncio in Python to scrape several products at the same time. A simple orchestrator might look like this:
# orchestrator.py
import asyncio
from price_scraper import price_scraper
from url_scraper import url_scraper
async def orchestrator(search_query: str, max_pages: int = None) -> list[dict]:
# Step 1: Scrape product URLs based on the search query
product_urls = await url_scraper(search_query, max_pages)
print(f"Total product URLs found: {len(product_urls)}")
# Step 2: For each product URL, scrape the price and other details
tasks = [price_scraper(url) for url in product_urls]
product_data = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
return product_data
if __name__ == "__main__":
search_query = "2024 macbook pro m4 max 16 inch"
max_pages = 2 # Limit to first 2 pages for testing
products_data = asyncio.run(orchestrator(search_query, max_pages))
print(f"Scraped data for {len(products_data)} products")Congrats, you can now scrape Amazon prices at scale! 🎊

Every Web Scraper Must Use These 4 Techniques
Four Python techniques that will vastly improve your web scrapers.
Read Full Story
How to Use Async Python Functions in AWS Lambda in 2026
Quick guide on how to use async Python functions in AWS Lambda
Read Full Story